
こんにちは。takapy(@takapy0210)です。
本エントリは言語処理100本ノック2020の6章を解いてみたので、それの備忘です。
途中まで解いて放置していました()が、続きをやる機会を得たので簡単な解説をつけながら紹介していきます。
例によってコードはGithubに置いてあります。
第6章: 機械学習
本章では,Fabio Gasparetti氏が公開しているNews Aggregator Data Setを用い,ニュース記事の見出しを「ビジネス」「科学技術」「エンターテイメント」「健康」のカテゴリに分類するタスク(カテゴリ分類)に取り組む.
50. データの入手・整形
""" News Aggregator Data Setをダウンロードし、以下の要領で学習データ(train.txt),検証データ(valid.txt),評価データ(test.txt)を作成せよ. 1. ダウンロードしたzipファイルを解凍し,readme.txtの説明を読む. """ import zipfile with zipfile.ZipFile('NewsAggregatorDataset.zip') as existing_zip: existing_zip.extractall()
zipfileを用いて解凍します。
""" News Aggregator Data Setをダウンロードし、以下の要領で学習データ(train.txt),検証データ(valid.txt),評価データ(test.txt)を作成せよ. 2. 情報源(publisher)が”Reuters”, “Huffington Post”, “Businessweek”, “Contactmusic.com”, “Daily Mail”の事例(記事)のみを抽出する. 3. 抽出された事例をランダムに並び替える. 4. 抽出された事例の80%を学習データ,残りの10%ずつを検証データと評価データに分割し,それぞれtrain.txt,valid.txt,test.txtというファイル名で保存する. ファイルには,1行に1事例を書き出すこととし,カテゴリ名と記事見出しのタブ区切り形式とせよ(このファイルは後に問題70で再利用する). 学習データと評価データを作成したら,各カテゴリの事例数を確認せよ """ import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 2. df = pd.read_csv('newsCorpora.csv', header=None, sep='\t', names=['id', 'title', 'url', 'publisher', 'category', 'story', 'hostname', 'timestamp']) cols = ['Reuters', 'Huffington Post', 'Businessweek', 'Contactmusic.com', 'Daily Mail'] df = df[df['publisher'].isin(cols)] # 3. df = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=42).reset_index(drop=True) print(df.head()) # 4. # カテゴリに分類するタスク(カテゴリ分類)に取り組む.とあるので、カテゴリで層化抽出する. train, test = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=df['category']) valid, test = train_test_split(test, test_size=0.5, random_state=42, stratify=test['category']) # データの保存 train.to_csv('train.txt', sep='\t', index=False) valid.to_csv('valid.txt', sep='\t', index=False) test.to_csv('test.txt', sep='\t', index=False) print('train ---- ', train.shape) print(train['category'].value_counts()) print('valid ---- ', valid.shape) print(valid['category'].value_counts()) print('test ----', test.shape) print(test['category'].value_counts())
カテゴリを予測するモデルを生成するので、train_test_splitのstratifyにカテゴリを指定して分割しています。
実行結果
id title ... hostname timestamp 0 173934 Taco Bell reveals 'secret' ingredients of myst... ... www.dailymail.co.uk 1398870059991 1 41713 RPT-UPDATE 2-Carlyle hires JPMorgan's Cavanagh... ... www.reuters.com 1395771699595 2 322477 Argentina Deposits $1 Billion For June 30 Bond... ... www.businessweek.com 1403853546347 3 114448 Banksy art work showing government agents spyi... ... www.dailymail.co.uk 1397518333460 4 178913 An acrobatic stunt went horribly wrong on Sund... ... www.dailymail.co.uk 1399320829491 [5 rows x 8 columns] train ---- (10672, 8) b 4502 e 4223 t 1219 m 728 Name: category, dtype: int64 valid ---- (1334, 8) b 562 e 528 t 153 m 91 Name: category, dtype: int64 test ---- (1334, 8) b 563 e 528 t 152 m 91 Name: category, dtype: int64
51. 特徴量抽出
""" 51. 特徴量抽出 学習データ,検証データ,評価データから特徴量を抽出し,それぞれtrain.feature.txt,valid.feature.txt,test.feature.txtというファイル名で保存せよ. なお,カテゴリ分類に有用そうな特徴量は各自で自由に設計せよ.記事の見出しを単語列に変換したものが最低限のベースラインとなるであろう. """ import pandas as pd import pickle import texthero as hero from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', 'valid': 'valid.txt', 'test': 'test.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') # データチェック for k in inputs.keys(): print(k, '---', dfs[k].shape) print(dfs[k].head()) return dfs def preprocess(text) -> str: """前処理""" clean_text = hero.clean(text, pipeline=[ hero.preprocessing.fillna, hero.preprocessing.lowercase, hero.preprocessing.remove_digits, hero.preprocessing.remove_punctuation, hero.preprocessing.remove_diacritics, hero.preprocessing.remove_stopwords ]) return clean_text class FeatureExtraction(): def __init__(self, min_df=1, max_df=1) -> None: self.tfidf_vec = TfidfVectorizer(min_df=min_df, max_df=max_df, ngram_range=(1, 2)) def fit(self, input_text) -> None: self.tfidf_vec.fit(input_text) def transform(self, input_text) -> pd.DataFrame: tfidf_vec = self.tfidf_vec.transform(input_text) return tfidf_vec if __name__ == "__main__": dfs = load_data() # trainとtestを生成 train = pd.concat([dfs['train'], dfs['valid']], axis=0).reset_index(drop=True) test = dfs['test'] # 前処理 train['clean_title'] = train[['title']].apply(preprocess) test['clean_title'] = test[['title']].apply(preprocess) # 特徴量抽出 feat = FeatureExtraction(min_df=10, max_df=0.1) feat.fit(train['clean_title']) X_train = feat.transform(train['clean_title']) X_test = feat.transform(test['clean_title']) pickle.dump(feat.tfidf_vec, open('tfidf_vec.pkl', 'wb')) # 推論時にも使用するため、保存 # DFに変換 X_train = pd.DataFrame(X_train.toarray(), columns=feat.tfidf_vec.get_feature_names()) X_test = pd.DataFrame(X_test.toarray(), columns=feat.tfidf_vec.get_feature_names()) # 分割して保存 X_valid = X_train[len(dfs['train']):].reset_index(drop=True) X_train = X_train[:len(dfs['train'])].reset_index(drop=True) X_train.to_csv('X_train.txt', sep='\t', index=False) X_valid.to_csv('X_valid.txt', sep='\t', index=False) X_test.to_csv('X_test.txt', sep='\t', index=False) print('X_train ---- ', X_train.shape) print('X_valid ---- ', X_valid.shape) print('X_test ---- ', X_test.shape)
texthere*1を用いてテキストの前処理を行っています。
特徴量抽出はシンプルにTFIDFを使いました。
FeatureExtractionクラスを生成して、fit()とtrainform()を分けることで、検証データに含まれるテキストは含まれないようにしています。
また、TfidfVectorizerのオブジェクトは以降のコードで使用するため、pkl形式で出力しています。
実行結果
train --- (10672, 8)
id title ... hostname timestamp
0 104130 UPDATE 1-Outkast goes back to 1990s hip hop at... ... www.reuters.com 1397300285495
1 353755 China's Stocks Head for Weekly Gain on Economi... ... www.businessweek.com 1404455149471
2 10240 Rare Diamond Shows Earth's Interior Is All Wet... ... www.huffingtonpost.com 1394715425065
3 208228 China Credit Gauge Declines as Officials Seek ... ... www.businessweek.com 1399970872744
4 288066 Angelina Jolie, Daniel Day Lewis & Dame Maggie... ... www.contactmusic.com 1402817031792
[5 rows x 8 columns]
valid --- (1334, 8)
id title ... hostname timestamp
0 230506 PRECIOUS-Gold ends flat as S&P 500 rises; plat... ... in.reuters.com 1400683341700
1 8444 CORRECTED-China Premier Li calls for relevant ... ... in.reuters.com 1394707522801
2 132330 Asia stocks subdued, Nikkei weak on profit taking ... www.businessweek.com 1397825631720
3 74570 Is 'How I Met Your Mother' The Best Ensemble C... ... www.contactmusic.com 1396349515070
4 56261 Russia says Ukrainian troops loyal to Kiev hav... ... www.reuters.com 1396011284905
[5 rows x 8 columns]
test --- (1334, 8)
id title ... hostname timestamp
0 306565 T-Mobile Just Did What Amazon's Fire Phone Cou... ... www.businessweek.com 1403198584880
1 228972 Seth McFarlane takes aim at western genre ... www.dailymail.co.uk 1400653319735
2 62224 Home > Kim Kardashian > Kim Kardashian To Try ... ... www.contactmusic.com 1396074886259
3 322698 GoPro's IPO priced at $24 per share: underwriter ... www.reuters.com 1403854662724
4 76854 Facebook's Mark Zuckerberg earned $3.3billion ... ... www.dailymail.co.uk 1396367931628
X_train ---- (10672, 2364)
X_valid ---- (1334, 2364)
X_test ---- (1334, 2364)
52. 学習
""" 52. 学習 51で構築した学習データを用いて,ロジスティック回帰モデルを学習せよ. """ import pandas as pd import pickle from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', 'X_train': 'X_train.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() assert dfs['train'].shape[0] == dfs['X_train'].shape[0], '長さが不正です' # モデルの学習 lg = LogisticRegression(random_state=42, max_iter=10000) lg.fit(dfs['X_train'], dfs['train']['category']) # モデルの保存 pickle.dump(lg, open('logreg.pkl', 'wb'))
ここは特に工夫点はないです。素直に学習させています。
53. 予測
""" 53. 予測 52で学習したロジスティック回帰モデルを用い,与えられた記事見出しからカテゴリとその予測確率を計算するプログラムを実装せよ. """ import pickle import numpy as np import pandas as pd import texthero as hero class PredictAPI(): def __init__(self): self.tfidf = pickle.load(open('tfidf_vec.pkl', 'rb')) self.logreg = pickle.load(open('logreg.pkl', 'rb')) def preprocess(self, input_text): """前処理""" clean_text = hero.clean(input_text, pipeline=[ hero.preprocessing.fillna, hero.preprocessing.lowercase, hero.preprocessing.remove_digits, hero.preprocessing.remove_punctuation, hero.preprocessing.remove_diacritics, hero.preprocessing.remove_stopwords ]) return clean_text def transform(self, input_text): clean_text = self.preprocess(input_text) tfidf_vec = self.tfidf.transform(clean_text) return tfidf_vec def predict(self, input_text): tfidf_vec = self.transform(input_text) # 推論 predict = [np.max(self.logreg.predict_proba(tfidf_vec), axis=1), self.logreg.predict(tfidf_vec)] return predict def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() # テキストを与えるとそのカテゴリを予測できるようにする api = PredictAPI() pred = api.predict(dfs['train']['title']) dfs['train']['pred_proba'] = pred[0] dfs['train']['pred'] = pred[1] print(dfs['train'][['title', 'category', 'pred_proba', 'pred']].head())
ここは実際のAPIをイメージして、生のテキストデータをapiに渡して推論できるようにPredictAPIクラスを生成しています。
(※以降のコードにもPredictAPIが出現します)
実行結果
title category pred_proba pred 0 UPDATE 1-Outkast goes back to 1990s hip hop at... e 0.881668 e 1 China's Stocks Head for Weekly Gain on Economi... b 0.982703 b 2 Rare Diamond Shows Earth's Interior Is All Wet... t 0.729923 t 3 China Credit Gauge Declines as Officials Seek ... b 0.944189 b 4 Angelina Jolie, Daniel Day Lewis & Dame Maggie... e 0.942834 e
54. 正解率の計測
""" 54. 正解率の計測Permalink 52で学習したロジスティック回帰モデルの正解率を,学習データおよび評価データ上で計測せよ. """ import pickle import numpy as np import pandas as pd import texthero as hero class PredictAPI(): def __init__(self): self.tfidf = pickle.load(open('tfidf_vec.pkl', 'rb')) self.logreg = pickle.load(open('logreg.pkl', 'rb')) def preprocess(self, input_text): """前処理""" clean_text = hero.clean(input_text, pipeline=[ hero.preprocessing.fillna, hero.preprocessing.lowercase, hero.preprocessing.remove_digits, hero.preprocessing.remove_punctuation, hero.preprocessing.remove_diacritics, hero.preprocessing.remove_stopwords ]) return clean_text def transform(self, input_text): clean_text = self.preprocess(input_text) tfidf_vec = self.tfidf.transform(clean_text) return tfidf_vec def predict(self, input_text): tfidf_vec = self.transform(input_text) # 推論 predict = [np.max(self.logreg.predict_proba(tfidf_vec), axis=1), self.logreg.predict(tfidf_vec)] return predict def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', 'test': 'test.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() # テキストを与えるとそのカテゴリを予測できるようにする api = PredictAPI() train_score = api.logreg.score(api.transform(dfs['train']['title']), dfs['train']['category']) test_score = api.logreg.score(api.transform(dfs['test']['title']), dfs['test']['category']) print(f'train score: {train_score}') print(f'test score: {test_score}')
シンプルな特徴量の割にはそこそこの精度がでています。
実行結果
train score: 0.9284107946026986 test score: 0.8755622188905547
55. 混同行列の作成
""" 55. 混同行列の作成 52で学習したロジスティック回帰モデルの混同行列(confusion matrix)を,学習データおよび評価データ上で作成せよ. """ import pickle import numpy as np import pandas as pd import texthero as hero from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix class PredictAPI(): def __init__(self): self.tfidf = pickle.load(open('tfidf_vec.pkl', 'rb')) self.logreg = pickle.load(open('logreg.pkl', 'rb')) def preprocess(self, input_text): """前処理""" clean_text = hero.clean(input_text, pipeline=[ hero.preprocessing.fillna, hero.preprocessing.lowercase, hero.preprocessing.remove_digits, hero.preprocessing.remove_punctuation, hero.preprocessing.remove_diacritics, hero.preprocessing.remove_stopwords ]) return clean_text def transform(self, input_text): clean_text = self.preprocess(input_text) tfidf_vec = self.tfidf.transform(clean_text) return tfidf_vec def predict(self, input_text): tfidf_vec = self.transform(input_text) # 推論 predict = [np.max(self.logreg.predict_proba(tfidf_vec), axis=1), self.logreg.predict(tfidf_vec)] return predict def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', 'test': 'test.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() # テキストを与えるとそのカテゴリを予測できるようにする api = PredictAPI() y_train = dfs['train']['category'] y_test = dfs['test']['category'] train_pred = api.predict(dfs['train']['title'])[1] test_pred = api.predict(dfs['test']['title'])[1] print(f'train confusion matrix:\n {confusion_matrix(y_train, train_pred)}') print(f'test confusion matrix:\n {confusion_matrix(y_test, test_pred)}')
実行結果
train confusion matrix: [[4366 71 8 57] [ 50 4159 5 9] [ 102 123 493 10] [ 191 127 11 890]] test confusion matrix: [[526 24 2 11] [ 17 506 2 3] [ 12 24 55 0] [ 43 27 1 81]]
56. 適合率,再現率,F1スコアの計測
""" 56. 適合率,再現率,F1スコアの計測 52で学習したロジスティック回帰モデルの適合率,再現率,F1スコアを,評価データ上で計測せよ. カテゴリごとに適合率,再現率,F1スコアを求め,カテゴリごとの性能をマイクロ平均(micro-average)とマクロ平均(macro-average)で統合せよ """ import pickle import numpy as np import pandas as pd import texthero as hero from sklearn.metrics import classification_report class PredictAPI(): def __init__(self): self.tfidf = pickle.load(open('tfidf_vec.pkl', 'rb')) self.logreg = pickle.load(open('logreg.pkl', 'rb')) def preprocess(self, input_text): """前処理""" clean_text = hero.clean(input_text, pipeline=[ hero.preprocessing.fillna, hero.preprocessing.lowercase, hero.preprocessing.remove_digits, hero.preprocessing.remove_punctuation, hero.preprocessing.remove_diacritics, hero.preprocessing.remove_stopwords ]) return clean_text def transform(self, input_text): clean_text = self.preprocess(input_text) tfidf_vec = self.tfidf.transform(clean_text) return tfidf_vec def predict(self, input_text): tfidf_vec = self.transform(input_text) # 推論 predict = [np.max(self.logreg.predict_proba(tfidf_vec), axis=1), self.logreg.predict(tfidf_vec)] return predict def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', 'test': 'test.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() # テキストを与えるとそのカテゴリを予測できるようにする api = PredictAPI() y_train = dfs['train']['category'] y_test = dfs['test']['category'] train_pred = api.predict(dfs['train']['title'])[1] test_pred = api.predict(dfs['test']['title'])[1] print(f'train classification_report:\n {classification_report(y_train, train_pred)}') print(f'test classification_report:\n {classification_report(y_test, test_pred)}')
classification_report便利ですね。
実行結果
train classification_report:
precision recall f1-score support
b 0.93 0.97 0.95 4502
e 0.93 0.98 0.96 4223
m 0.95 0.68 0.79 728
t 0.92 0.73 0.81 1219
accuracy 0.93 10672
macro avg 0.93 0.84 0.88 10672
weighted avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 10672
test classification_report:
precision recall f1-score support
b 0.88 0.93 0.91 563
e 0.87 0.96 0.91 528
m 0.92 0.60 0.73 91
t 0.85 0.53 0.66 152
accuracy 0.88 1334
macro avg 0.88 0.76 0.80 1334
weighted avg 0.88 0.88 0.87 1334
57. 特徴量の重みの確認
""" 57. 特徴量の重みの確認 52で学習したロジスティック回帰モデルの中で,重みの高い特徴量トップ10と,重みの低い特徴量トップ10を確認せよ. """ import pickle import numpy as np import pandas as pd def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'X_train': 'X_train.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() features = dfs['X_train'].columns.values index = [i for i in range(1, 11)] # モデルのロード logreg = pickle.load(open('logreg.pkl', 'rb')) for c, coef in zip(logreg.classes_, logreg.coef_): print(f'category: {c}') best10 = pd.DataFrame(features[np.argsort(coef)[::-1][:10]], columns=['TOP'], index=index).T worst10 = pd.DataFrame(features[np.argsort(coef)[:10]], columns=['LOW'], index=index).T print(pd.concat([best10, worst10], axis=0)) print('\n')
カテゴリはb = business, t = science and technology, e = entertainment, m = health なので、そこそこ直感的に重み付けされていそうです。
実行結果
category: b
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
TOP fed ecb bank stocks china euro dollar obamacare profit ipo
LOW ebola microsoft facebook virus heart video star aereo mother fda
category: e
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
TOP kardashian chris movie beyonce film star trailer kim paul miley
LOW us google china study gm billion buy sales apple microsoft
category: m
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
TOP ebola study cancer fda mers drug health cdc brain cases
LOW gm facebook apple deal sales twitter ceo bank fed climate
category: t
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
TOP google facebook apple microsoft climate nasa gm tesla comcast heartbleed
LOW stocks drug fed cancer percent american shares day ecb ukraine
58. 正則化パラメータの変更
""" 58. 正則化パラメータの変更Permalink ロジスティック回帰モデルを学習するとき,正則化パラメータを調整することで,学習時の過学習(overfitting)の度合いを制御できる. 異なる正則化パラメータでロジスティック回帰モデルを学習し,学習データ,検証データ,および評価データ上の正解率を求めよ.実験の結果は,正則化パラメータを横軸,正解率を縦軸としたグラフにまとめよ. """ import numpy as np import pandas as pd import pickle import texthero as hero from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score import matplotlib.pyplot as plt class PredictAPI(): def __init__(self, logreg_model): self.tfidf = pickle.load(open('tfidf_vec.pkl', 'rb')) self.logreg = logreg_model def preprocess(self, input_text): """前処理""" clean_text = hero.clean(input_text, pipeline=[ hero.preprocessing.fillna, hero.preprocessing.lowercase, hero.preprocessing.remove_digits, hero.preprocessing.remove_punctuation, hero.preprocessing.remove_diacritics, hero.preprocessing.remove_stopwords ]) return clean_text def transform(self, input_text): clean_text = self.preprocess(input_text) tfidf_vec = self.tfidf.transform(clean_text) return tfidf_vec def predict(self, input_text): tfidf_vec = self.transform(input_text) # 推論 predict = [np.max(self.logreg.predict_proba(tfidf_vec), axis=1), self.logreg.predict(tfidf_vec)] return predict def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', 'valid': 'valid.txt', 'test': 'test.txt', 'X_train': 'X_train.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() assert dfs['train'].shape[0] == dfs['X_train'].shape[0], '長さが不正です' C_candidate = [0.1, 1.0, 10, 100] result = [] y_train = dfs['train']['category'] y_valid = dfs['valid']['category'] y_test = dfs['test']['category'] for C in C_candidate: # モデルの学習 lg = LogisticRegression(random_state=42, max_iter=10000, C=C) lg.fit(dfs['X_train'], dfs['train']['category']) # 予測値の取得 api = PredictAPI(lg) train_pred = api.predict(dfs['train']['title'])[1] valid_pred = api.predict(dfs['valid']['title'])[1] test_pred = api.predict(dfs['test']['title'])[1] # 正解率の算出 train_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_train, train_pred) valid_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_valid, valid_pred) test_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, test_pred) # 結果の格納 result.append([C, train_accuracy, valid_accuracy, test_accuracy]) result = np.array(result).T plt.plot(result[0], result[1], label='train') plt.plot(result[0], result[2], label='valid') plt.plot(result[0], result[3], label='test') plt.ylim(0, 1.1) plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.xscale('log') plt.xlabel('C') plt.legend() plt.savefig('ans_58.png')
実行結果
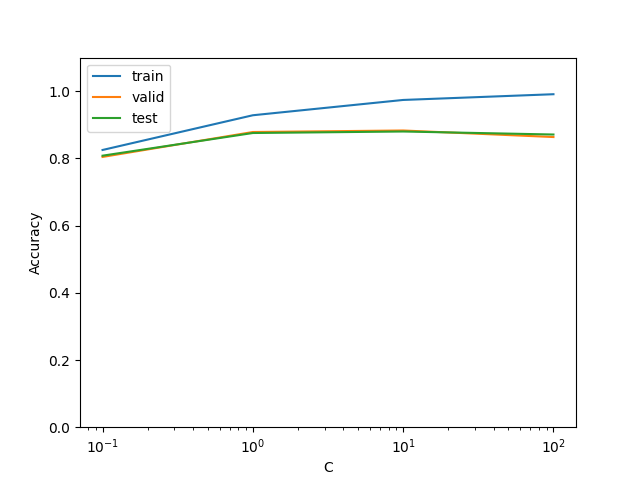
59. ハイパーパラメータの探索
""" 59. ハイパーパラメータの探索 学習アルゴリズムや学習パラメータを変えながら,カテゴリ分類モデルを学習せよ.検証データ上の正解率が最も高くなる学習アルゴリズム・パラメータを求めよ.また,その学習アルゴリズム・パラメータを用いたときの評価データ上の正解率を求めよ. """ import numpy as np import pandas as pd import pickle import texthero as hero from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score import optuna class PredictAPI(): def __init__(self, model): self.tfidf = pickle.load(open('tfidf_vec.pkl', 'rb')) self.model = model def preprocess(self, input_text): """前処理""" clean_text = hero.clean(input_text, pipeline=[ hero.preprocessing.fillna, hero.preprocessing.lowercase, hero.preprocessing.remove_digits, hero.preprocessing.remove_punctuation, hero.preprocessing.remove_diacritics, hero.preprocessing.remove_stopwords ]) return clean_text def transform(self, input_text): clean_text = self.preprocess(input_text) tfidf_vec = self.tfidf.transform(clean_text) return tfidf_vec def predict(self, input_text): tfidf_vec = self.transform(input_text) # 推論 predict = [np.max(self.model.predict_proba(tfidf_vec), axis=1), self.model.predict(tfidf_vec)] return predict def load_data() -> dict: """データの読み込み""" # 読み込むファイルを定義 inputs = { 'train': 'train.txt', 'valid': 'valid.txt', 'test': 'test.txt', 'X_train': 'X_train.txt', } dfs = {} for k, v in inputs.items(): dfs[k] = pd.read_csv(v, sep='\t') return dfs class HyperparameterSearch(): def __init__(self, dfs): self.dfs = dfs def objective_lg(self, trial): """最適化""" l1_ratio = trial.suggest_uniform('l1_ratio', 0, 1) C = trial.suggest_loguniform('C', 1e-4, 1e2) # モデルの学習 lg = LogisticRegression(random_state=42, max_iter=10000, penalty='elasticnet', solver='saga', l1_ratio=l1_ratio, C=C) lg.fit(self.dfs['X_train'], dfs['train']['category']) # 予測値の取得 api = PredictAPI(lg) valid_pred = api.predict(dfs['valid']['title'])[1] # 正解率の算出 valid_accuracy = accuracy_score(dfs['valid']['category'], valid_pred) return valid_accuracy def search_optuna(self): study = optuna.create_study(direction='maximize') study.optimize(self.objective_lg, timeout=3600) return study if __name__ == "__main__": # データのロード dfs = load_data() assert dfs['train'].shape[0] == dfs['X_train'].shape[0], '長さが不正です' # 最適化 tuner = HyperparameterSearch(dfs) study = tuner.search_optuna() # 結果の表示 print('Best trial:') trial = study.best_trial print(' Value: {:.3f}'.format(trial.value)) print(' Params: ') for key, value in trial.params.items(): print(' {}: {}'.format(key, value))
optuna*2を用いてパラメータ探索を行いました。(上記のコードは結構時間がかかります)
結果としては
- l1_ratio: 0.190283773569564
- C: 2.97492047697017
が良いパラメータとして推定されました。
実行結果
.....
[I 2021-06-05 16:45:50,322] Trial 25 finished with value: 0.8823088455772113 and parameters: {'l1_ratio': 0.39957785978633487, 'C': 2.820148509505984}. Best is trial 14 with value: 0.8845577211394303.
[I 2021-06-05 16:46:14,130] Trial 26 finished with value: 0.7931034482758621 and parameters: {'l1_ratio': 0.4399758132783767, 'C': 0.17773660929932344}. Best is trial 14 with value: 0.8845577211394303.
[I 2021-06-05 16:49:42,323] Trial 27 finished with value: 0.8718140929535232 and parameters: {'l1_ratio': 0.22609331565604585, 'C': 22.130119756833977}. Best is trial 14 with value: 0.8845577211394303.
Best trial:
Value: 0.885
Params:
l1_ratio: 0.190283773569564
C: 2.97492047697017
実際にこのパラメータで再度学習させてみると下記のようにスコアが改善しました。
train score: 0.9562406296851574(元々のスコア:0.9284107946026986) test score: 0.883808095952024(元々のスコア:0.8755622188905547)